Biological Diversity How Do We Explain Differences Among Organisms
E A group that has an open circulatory system. There are two mechanisms by which speciation occur because of this reproductive isolation.
The Diversity Of Life Biology For Majors Ii
Some organisms capture energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy in food.

. Is part of Smithsonian Science for the Classroom a brand new curriculum series by the Smithsonian Science Education Center. C Kingdom to which animal belongs. There are two constituents of species diversity.
Biodiversity is not evenly distributed rather it varies greatly across the globe as well as within regions. Up to 24 cash back explain biological diversity in terms of the Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection by examining the changes in and diversification of life since it first appeared on the Earth analyse how an accumulation of microevolutionary changes can drive evolutionary changes and speciation over time for example. All organisms use a source of energy for their metabolic activities.
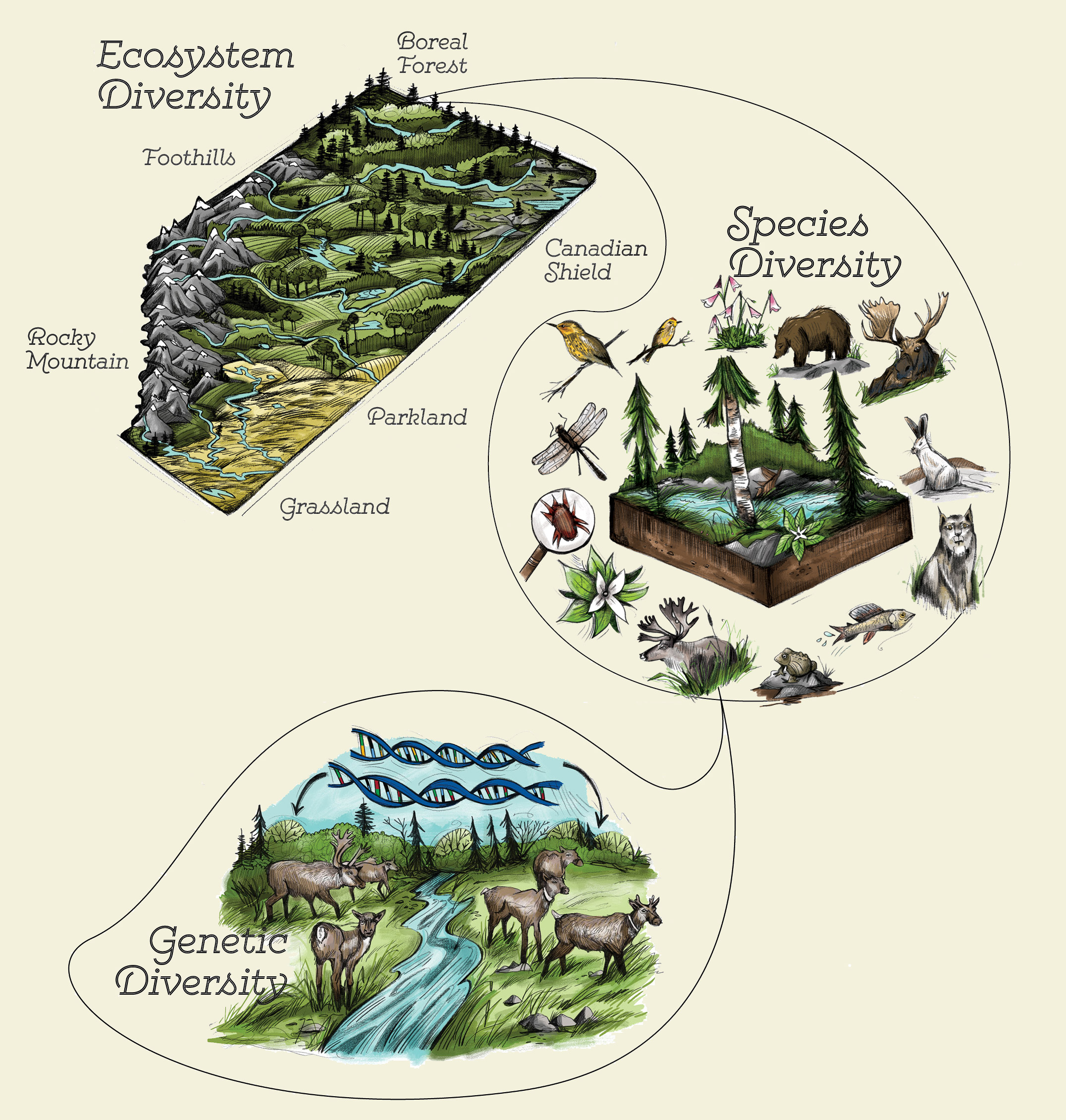
This measurement compares the diversity of species in an area with the total number of organisms in the same area. This includes diversity within species between species and ecosystems. Identify and name the following.
BASIC INFORMATION MICROBES They are the unicellular organisms which can not seen. In addition to diversity among species the concept of biodiversity includes the genetic diversity within species. Biological diversity is reflected in the range of species found in local and global environments and by subtle variations in characteristics found within individual species.
Biodiversity Is The Variability Among Living. It has a focus on life science with a secondary focus on Earth and space science. Consider the levels of organization of the biological world and create a diagram to place these items in order from the smallest level of organization to the most encompassing.
Humans have come up with ways of organizing or classifying biological diversity throughout human historyOrganisms can be classified according to any number of criteria including overall similarities colors ecological functions etc. Up to 24 cash back Unit A. BIological diversity or biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of living organisms on the planet.
Then using similarities and differences among the organisms make a hypothesis about their relatedness. Solution for How will you explain that using genetic differences among populations or species to. Genetic spe- cies and ecosystem diversity.
Genetic variations can arise from gene variants also called mutations or from a normal process in which genetic material is rearranged as a cell is getting ready to divide known as genetic recombination. Evolutionary theory explains that biological diversity results from the descendants of local or migrant predecessors becoming adapted to their diverse environments. The variety of life on Earth its biological diversity is commonly referred to as biodiversity.
The diversity of life on Earth is a result of mutations or random changes in hereditary material over. Biodiversity is the variability among living organisms from all sources including terrestrial marine and other aquatic ecosystems. D An example of a moneran and an animal with the pseudocoelom.
Each definition is useful depending on the situation or questions asked but the biological species concept helps us focus on the differences among the groups of organisms and how they are reproductively isolated from one another. Others use chemical energy in molecules they take in as food Figure 114. Up to 24 cash back To determine the biological diversity of an area biologists use a measure- ment called the diversity index.
Likewise genetic variety within a plant. What Explains Similarities and Differences Between Organisms. One example is our own species for we differ in a wide variety of characteristics that are partly or wholly genetically determined including height weight skin and eye colour behavioral traits and resistance to various diseases.
Species diversity is the most common level of diversity. Organisms continually adapt to their environments and the diversity of environments that exists promotes a diversity of organisms adapted to them. Years of evolutionary history in order to understand the extraordinary events that have ultimately resulted in the biological diversity we see around us today.
A Organisms that use dead and decaying organic material as food. Biological Diversity Social and Environmental Emphasis Overview. It is aligned to a group of grade 3 standards.
The three main aspects of biodiversity include genetic diversity species diversity and ecosystem diversity. The diversity of living organisms on earth is truly astounding almost overwhelming. Evolution and Diversity - Opportunities in Biology - NCBI Bookshelf.
Among other factors the diversity of all living things depends on temperature precipitation altitude soils geography and the presence of other speciesThe study of the spatial distribution of organisms species and ecosystems is the science of biogeography. Number of different species present in an ecosystem. Evolution and diversity result from the interactions between organisms and their environments and the consequences of these interactions over long periods of time.
It is normal for some places to have a higher diversity index than others. Despite the fact that there are not enough genetic and biological differences among humans to uphold the idea of distinct races. Genetic variations that alter gene activity or protein function can introduce different traits in an organism.
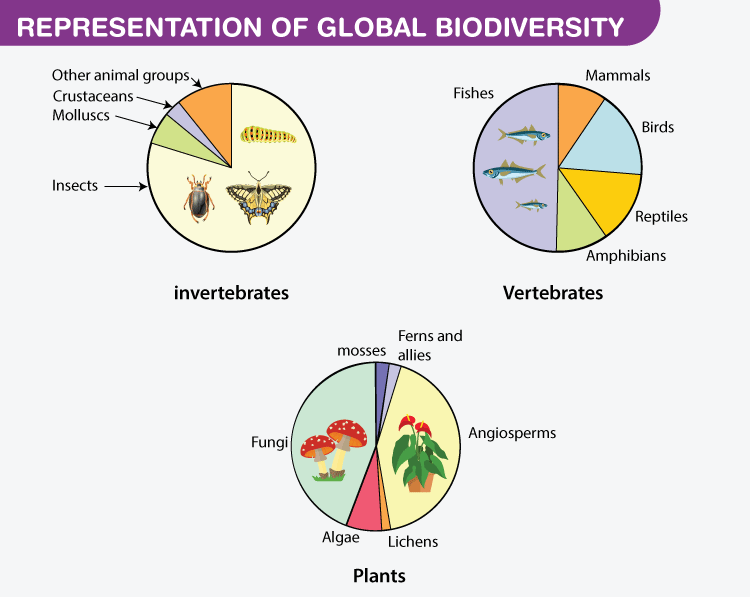
The number of species of plants animals and microorganisms the enormous diversity of genes in these species the different ecosystems on the planet such as deserts rainforests and coral reefs are all part of a biologically diverse Earth. Species diversity is defined as the number of different species present in an ecosystem and relative abundance of each of those species Diversity is greatest when all the species present are equally abundant in the area. Ecologists tend to focus on three lev- els of biological diversity.
Biological Diversity in General Encompasses all variation in life Encompasses all levels of the biological hierarchy Characterization of biological diversity species genetics communities and ecosystems Tradeoffs may exist among different dimensions Brook Milligan What is. B Cell walls of fungi are made up of this special type of sugar. Skin cell planet Earth elephant tropical rainforest water.
This explanation can be tested by examining present species and local fossils to see whether they have similar structures which would indicate how one is derived from the other.

Soil Biodiversity Esdac European Commission

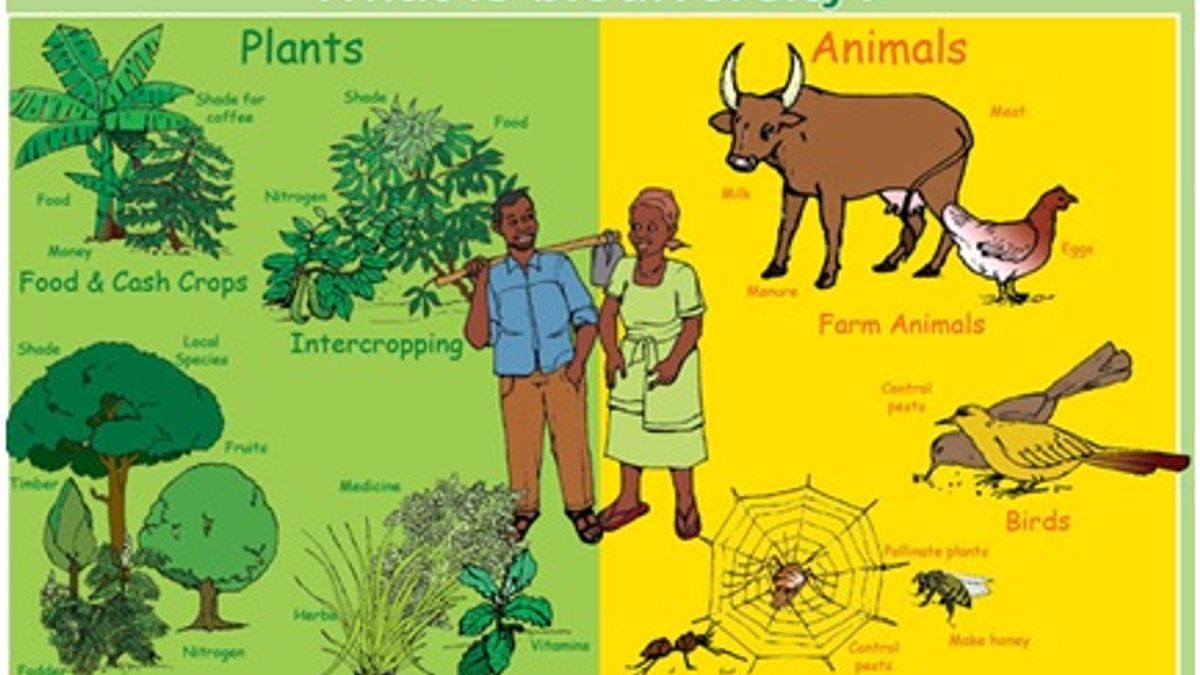
Biodiversity In Plants And Animals Its Importance

Biological Diversity Current Biology

Ngss Ms Ls4 2 Biological Evolution Unity And Diversity Comparative Anatomy Life Science Middle School Ngss Science Ngss
What Is The Meaning Of Biodiversity In Simple Words

The Diversity Of Life Biology For Majors Ii

What Are The Three Types Of Biodiversity
Species Diversity Definition Importance Examples Threats Conservation

Biodiversity Kindergarten Lesson Plan Kindergarten Lesson Plans Lesson Planet Biodiversity

Reversing The Loss Of Biological Diversity Money Talks Envirobites
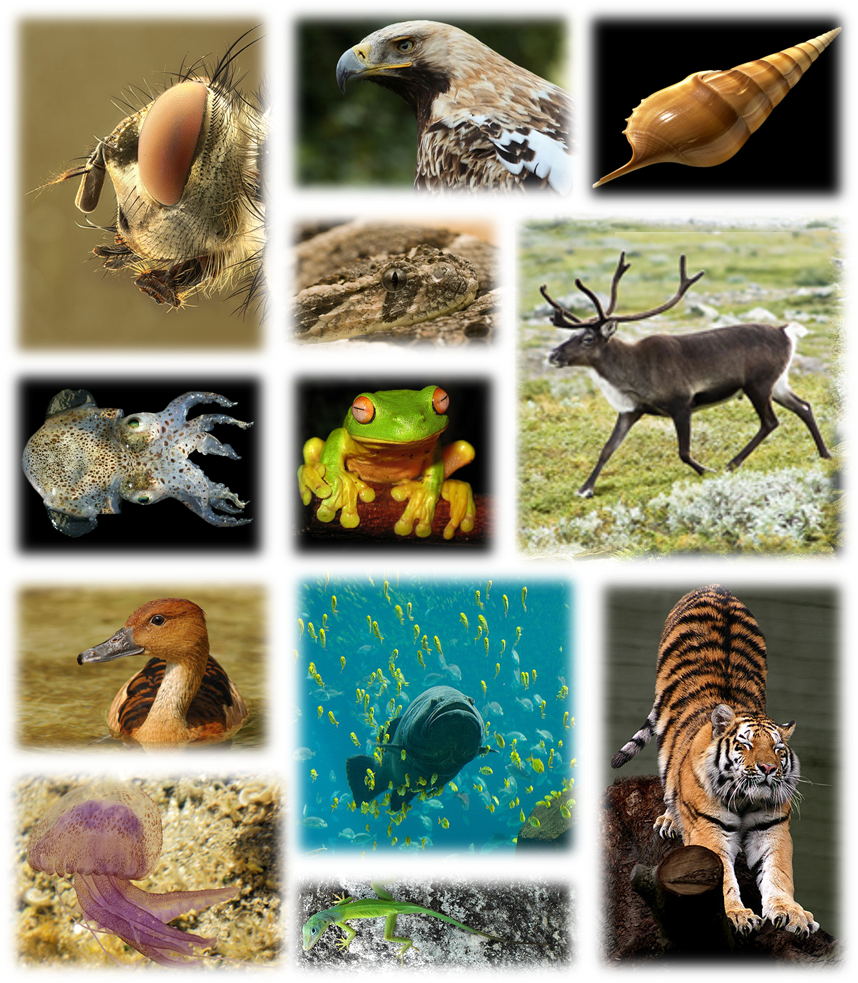









Comments
Post a Comment